10.31 제너릭을 이용해 사용자 지정 타입 활용하기 (where문 비활용)
C#/실습 2019. 10. 31. 14:10예제:

코드:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace _10._31_step1
{
class App
{
public App()
{
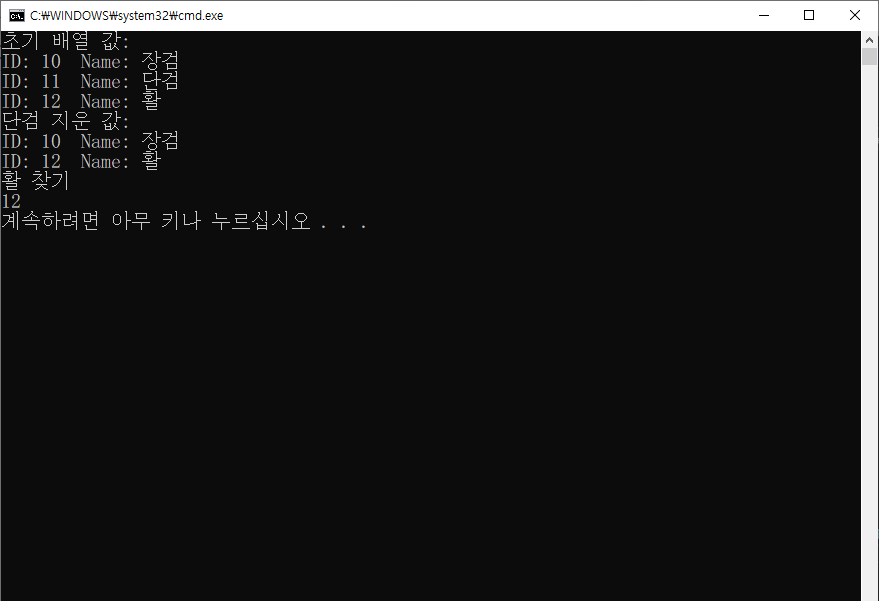
Inventory<Item> inventory = new Inventory<Item>(10);
inventory.AddItem(new Item(10, "장검"));
inventory.AddItem(new Item(11, "단검"));
inventory.AddItem(new Item(12, "활"));
Console.WriteLine("초기 배열 값:");
inventory.RemoveItem("단검");
Console.WriteLine("단검 지운 값:");
Console.WriteLine("활 찾기");
Console.WriteLine(inventory.FindItem("활").Id);
}
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#4f4f4ftext-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace _10._31_step1
{
class Inventory <T> //where T: Item //Item 클래스나 Item 파생 클래스만 들어올 수 있다.
{
private T[] items;
public T this[int i]
{
get
{
return this.items[i];
}
}
public void AddItem(T item)
{
{
if(items[i] == null)
{
items[i] = item;
break;
}
}
}
public void RemoveItem(string name)
{
{
if(items[i] is Item)
{
if((items[i] as Item).Name == name)
{
items[i] = default;
}
}
}
}
public T FindItem(string name)
{
{
if (items[i] is Item)
{
if ((items[i] as Item).Name == name)
{
return items[i];
}
continue;
}
continue;
}
return default;
}
public void Print()
{
foreach(var data in items)
{
if(data != null && data is Item)
{
Item item = data as Item;
}
}
}
public Inventory(int capacity)
{
this.items = new T[capacity];
}
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#4f4f4ftext-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace _10._31_step1
{
class Item
{
public int Id { get; private set; }
public string Name { get; private set; }
public Item(int id, string name)
{
this.Id = id;
this.Name = name;
}
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#4f4f4ftext-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
'C# > 실습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 11.05 Unity 객체, 이벤트, prefeb파일 (2) | 2019.11.05 |
|---|---|
| 10.31 인덱서를 이용해 LinkedList 클래스 만들기 (0) | 2019.10.31 |
| 10.31 제너릭을 이용해 사용자 지정 타입 활용하기 (where문 활용) (0) | 2019.10.31 |
| 10.30 클래스로 LinkedList 구현하기 (메서드, 속성의 재귀호출) (0) | 2019.10.30 |
| 10.23 Stack 활용하기 (0) | 2019.10.24 |